Digital Twin of a Free-Electron Laser
Study of laser plasma acceleration processes addresses high requirements to the technical equipment and time consumption in numerical and experimental research. A demand on statistical and mathematical methods for inversion of the system state, comprehension of measurement data and quantification of data stability can only be done by a comprehensive machine learning based surrogate model for Laser-driven Plasma Accelerators.
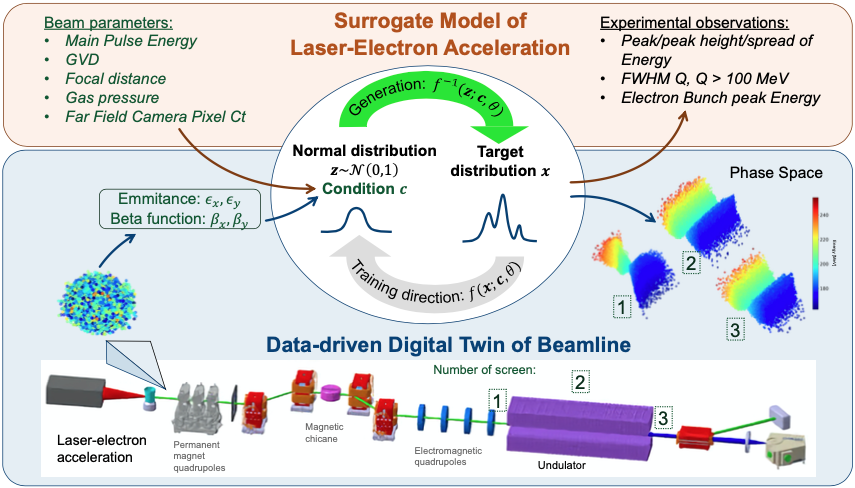
This surrogate potentially accelerates theoretical comprehension of the beamline, in terms of design space exploration and promises reliable in-situ analysis of experimental data which leads novel guidance mechanisms for future Laser-driven Plasma Accelerators. The main aim of our work is to elaborate surrogate models for Free Electron Laser by virtue of that one could unveil beam dynamics(in terms of particle data) on the scope of collected diagnostic.
Achieved results for the first stage of FEL: acceleration of particles in LWFA regime, demonstrate ability to learn an approximation of data-dependent posterior distribution by conditional inventible neural networks. The further derived model is able to describe an electron bunch transformation in the FEL beam transport in terms of phase space particle distribution based on its initial parameters: divergence and size. This step opens a perspective to a potential elaborated model that could use obtained diagnostics for reconstruction of beam at any point in the FEL.
Team
- Ankush Checkervarty
- Vedhas Sadanand Pandit
- Fong-Lin Wu
Publications
Miethlinger, M., Hoffmann, N., Kluge, T. (2022). Acceptance Rates of Invertible Neural Networks on Electron Spectra from Near-Critical Laser-Plasmas: A Comparison. Applications of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in High Performance Computing @ 14th PPAM. paper
Willmann A., Cabadag J. C., Chang Y.-Y., Pausch R., Ghaith A., Debus A., Irman A., Bussmann M., Schramm U., Hoffmann N. (2022). Learning Electron Bunch Distribution along a FEL Beamline by Normalising Flows. Machine Learning and the Physical Sciences @ NeurIPS 2022. paper
Bethke, F., Pausch, R., Stiller, P., Debus, A., Bussmann, M., Hoffmann, N. (2021). Invertible Surrogate Models: Joint Surrogate Modelling and Reconstruction of Laser Wakefield Acceleration by Invertible Neural Networks. Simulation with Deep Learning @ ICLR. paper
Willmann, A., Stiller, P., Debus, A., Irman, A., Pausch, R., Chang Y.-Y., Bussmann, M., Hoffmann, N. (2021). Data-Driven Shadowgraph Simulation of a 3D Object. Simulation with Deep Learning @ ICLR 2021. paper
